TEXTILE FIBER MARKET
Home > Textile fiber market
Currently, polyacrylonitrile is used in the textile industry in the form of fibers labeled as "acrylic." Properties such as high electrical resistance, elasticity, and low density make acrylic fiber a widely used industrial material, especially in the clothing industry. Another application that has been growing recently is its use in home furnishings.
In 2024, global consumption of acrylic fibers was estimated at approximately 1.6 million tons. This volume was once much higher and has been losing ground to other synthetic fibers, mainly polyester. As for market value, it is estimated at US$5.8 billion in 2025, but should reach US$7 billion in 2034 with a growth of 2.1% per year.
Acrylic Fiber Markets (in billions of dollars):
Source:
https://www.marketgrowthreports.com/
However, its consumption should remain relatively stable for the next 10 years, as there are few fibers with similar properties and lower cost to replace PAN in its current applications.
The region with the highest concentration of acrylic fiber production is China, which accounts for approximately 40% of world production, followed by the regions encompassing the Middle East and Africa, with 20%.
The largest producing companies in the world, responsible for approximately 50% of global capacity, are:
• AKSA Akrilik (Turkey), which has a production capacity of 355,000 T/A. The company has a 19% share of the global acrylic fiber market and 70% of the domestic market.
• Jilin Qifeng Chemical (China), with a capacity of 150,000 T/A.
• Aditya Birla Group, which produces the Birlacril brand through Thai Acrylic Fiber Co Ltd, in Thailand, with a capacity of 108,000 T/A.
• SPC Sinopec (China), which has a capacity of 113,200 T/A.
Other companies with capacities below 100,000 T/A are:
• CNPC (China)
• Companhia Sudamericana de Fibras (SDF) (Perú)
• Exlan Toyobo Group (Japan)
• Formosa Plastics Corp (Taiwan)
• Indian Acrylics (India)
• Kaltex (Mexico)
• Kaneka Corporation (Japan)
• Pasupati Acrylon (India)
• Polyacryl Iran Corp (Iran)
• Polymir (Belarus)
• Taekwang Industrial (South Korea)
• Tong-Hwa Synthetic Fiber (Taiwan)
• Toray (Japan)
• Vardhman Acrylics (India)
• Yousuf Dewan (Pakistan)
In the last 10 years, several companies in the sector have closed, and we can highlight:
• DOLAN GmbH (Germany)
• DRALON GmbH (Germany)
• Mitsubishi Rayon Group (Japan)
• Crylor (Brazil)
• Jiangsu Zhongxin Resources Group (China)
• SGL Carbon (Ex-Fisipe) (Portugal)
• Montefibre (Spain)
• Alexandria Fiber Co (Egypt)
The synthetic fiber market is dominated by polyester, followed by nylon (polyamide), polypropylene, and acrylic fibers in fourth place with a production of 1.6 million tons per year in 2025.
In Brazil, there were two factories in the past: Companhia Sudamerica de Fibras (SDF), located in the Camaçari Petrochemical Complex (BA), which used Mitsubishi Rayon dry spinning technology, and Radicifibras in São José dos Campos (SP), which employed Dupont wet spinning technology, having ceased its production of "Crylor" fiber in 2013.
Throughout the Americas, there are only two companies producing acrylic fibers: Companhia Sudamerica de Fibras (SDF), located in Callao (Peru), and Kaltex, located in Altamira, Mexico.
In relation to the global market for synthetic fibers, which is around 80 million tons per year and is mainly dominated by polyester, the share of acrylic fibers is relatively small, but has remained constant over the last decade, at around 1.5 million tons per year, occupying niche applications where their differentiated properties compared to polyester and nylon make acrylic fibers advantageous, such as high resistance to degradation by sunlight, thermal insulation, resistance to organic solvents, and infusibility, similar to natural fibers such as silk and wool.
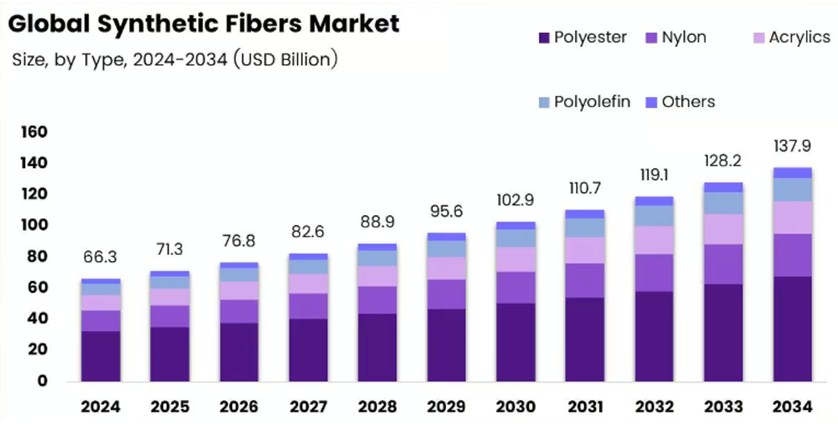
Global Synthetic Fiber Markets (in billions of dollars):
Source:
https://market.us/report/synthetic-fibers-market/
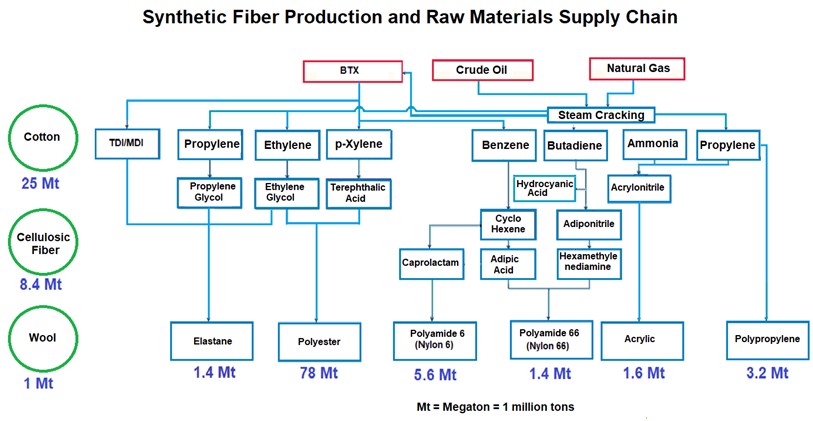
Global Synthetic and Natural Fiber Markets 2025 (in millions of tons) :